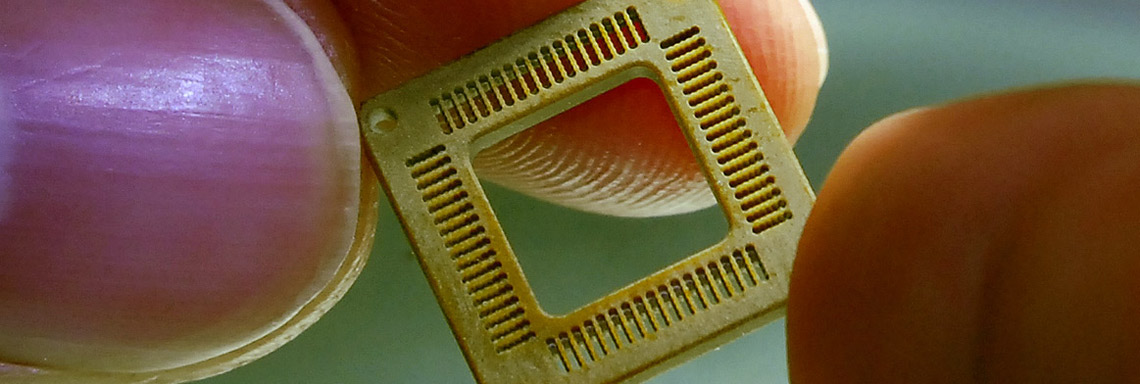
Micromachining is far from new, but the sheer volume of products and industries requiring micro-machined components is rapidly increasing. Complexity is growing while the sizes of components are shrinking. Micromachining is a niche within the machine shop industry that provides point on accuracy, short runs, condensed lead times and significant quick turn prototyping. One of the largest challenges in micromachining is finding cutting tools that can withstand high rpm’s, tolerate long cycles while holding precise repeatability.
Miniature, complex parts are much easier than in the past to have made by partnering with a micro-manufacturing company with wide ranging equipment such as: micro machine centers, CNC mills, and multiple types of turning centers with multi axis capabilities. Industries such as medical, aerospace, automotive and semiconductor can slash their time to market while keeping up with the ever changing technical challenges they face. The differences now show increase in volume requiring micromachining, the engineered composite materials used that can hold up in extreme conditions and decrease in turn times. While many machine shops attempt to expand into micromachining, it takes years of experience working with the exotic materials to be able to deliver as expected.
At this scale many variations such as thermal conditions, vibration and the cutting tools used could have an adverse effect on the ability to manufacture to the tight tolerances required. Companies need to develop new methods and technologies to meet these micromachining and manufacturing challenges.
There are several key areas where machining this small raises concerns:
- Accuracy impacted by environmental changes
- Repeatability and predictability of the machining process
- Internal and external vibration (machine and/or floor)
- Fluid dynamics dealing with cutting fluids
These variables become much more pronounced at the micro level and may be hard to control. Experienced machine shops will have processes in place that account for these changes to efficiently deliver the end piece.
There are many challenges that impact the cost of the micromachining process. Systems and equipment have been developed to accommodate the demands of the industry for more production capacity. These advancements in technology and equipment have made the micromachining process more affordable. The lathes and mills are smaller in size with the base and column cast from a proprietary granite co-polymer composite. These composites appear to offer higher vibration damping than traditional cast iron. It’s the demand for these micromachined short run items or prototype parts that is has driven growth of this industry sector. There will always be a demand for low-volume, quick turn runs, requiring a source for rapid prototyping requirements and pilot programs,. Companies will keep providing engineering services to help optimize customer’s designs for manufacturability and speed.
About Challenge Machine
Challenge Machine & Manufacturing Inc. is the premier precision contract manufacturer of micromachined solutions for the world’s most advanced industries. Driven by a challenge, every project we deliver adheres to the tightest tolerances, uses the most exotic materials, and meets the quickest turnarounds that our customers demand.
At Challenge Machine we make the impossible a reality.
